Difference between revisions of "PhoXi 3D scanners family"
| Line 142: | Line 142: | ||
Connect to the first scanner, then click menu -> network discovery and then click the second scanner you want to connect to. | Connect to the first scanner, then click menu -> network discovery and then click the second scanner you want to connect to. | ||
You will then have two tabs as you can see in the picture below and then you can change between the two tabs by clicking on them. | You will then have two tabs as you can see in the picture below and then you can change between the two tabs by clicking on them. | ||
| − | [[File:pane_wiki.png]] | + | [[File:pane_wiki.png|1100px]] |
| − | |||
;Using the PhoXi API | ;Using the PhoXi API | ||
Revision as of 09:06, 15 October 2018
This page contains technical description of PhoXi 3D Scanners. For scanning guide, see Scanning best practices.
Contents
General specification
| Light source | Visible red light (laser) |
| Wavelength | 638nm |
| Laser class | 3R (IEC / EN 60825-1, 2014) |
| Peak / CW Power | 314uW |
| Pulse Energy | 382nJ |
| Pulse Length | 960us |
| Projection angle horizontal | 47.5° ±1° |
| Projection angle vertical | 36.0° ±2° |
For model/size specific parameters see our product showcase.
Specification Parameters Explanation
- Depth Map resolution
- Maximum number of rendered points (the resolution of camera sensor)
- Point size
- The average distance between two neighboring points on the point cloud of a plane located in the focus distance of the camera. Alternatively, the square of the point size is the average surface sampled by one 3D point on the plane scanned in the focus distance of the camera.
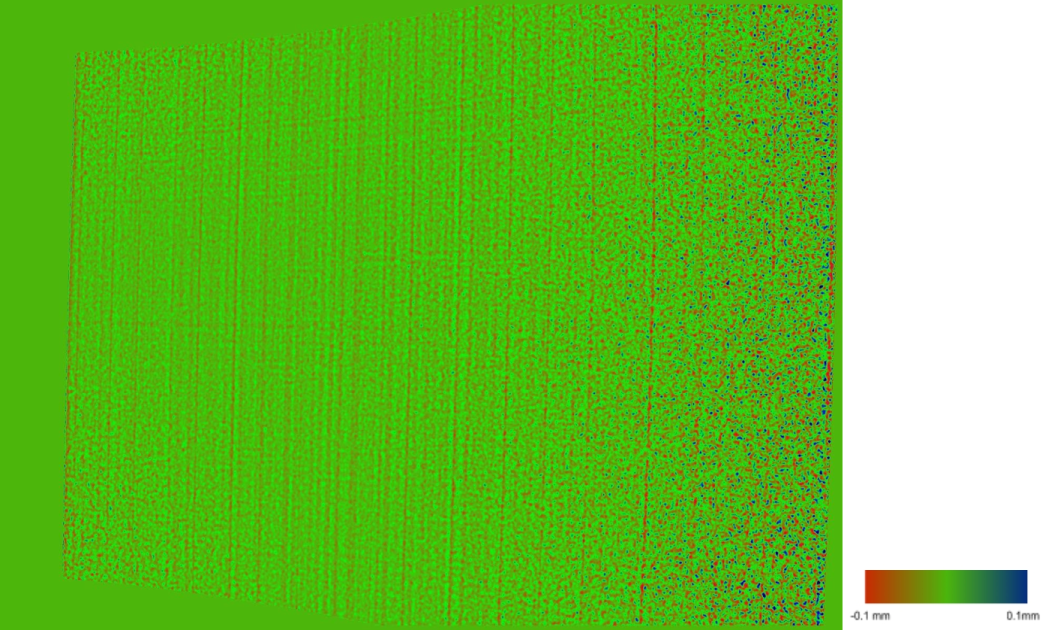
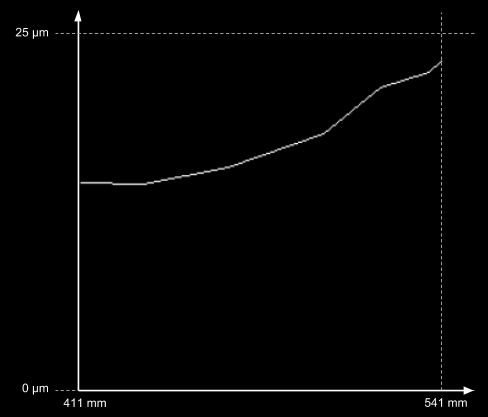
- Absolute accuracy
- The accuracy of point measurement as the result of device calibration (can be understood as the space deformation). It is the standard deviation of the measurement error in the whole measurement range of the device.
- Absolute accuracy is measured by scanning multiple planes at different distances from the scanner. Below you can see a scan of the plane done by the PhoXi 3D Scanner model S at the distance of 411mm. The red points are closer to the plane and the blue points are further away form the plane
- Absolute accuracy is the average distance of the 3D points from this plane.
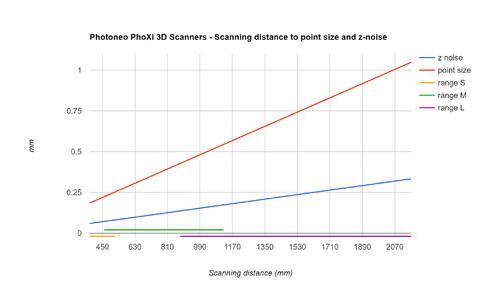
- Z noise
- The standard deviation of the noise (measured on a diffuse surface with 80 percent albedo). The noise level describes the quality of the sensor to capture local surface details. The noise distribution of our sensor is similar to Gaussian distribution. Can be understood as temporal noise.
- Below is a graph depicting the Standard deviation of depth (Z-noise) values of 3D points for different scanning distances for the PhoXi 3D Scanner model S.
- Equivalently, Z-noise can also be defined as the average distance of the 3D points from the average Z-value of the 3D points.
- FPS
- Maximum number of triggered frames per second, in fastest acquisition mode
- Data acquisition time - best case
- Fastest possible acquisition time
- Data acquisition time - worst case
- Longest expected acquisition time (bad lighting conditions, dark shiny objects)
- 3D points throughput
- Number of 3D points that can be reconstructed in a second in sequential scans
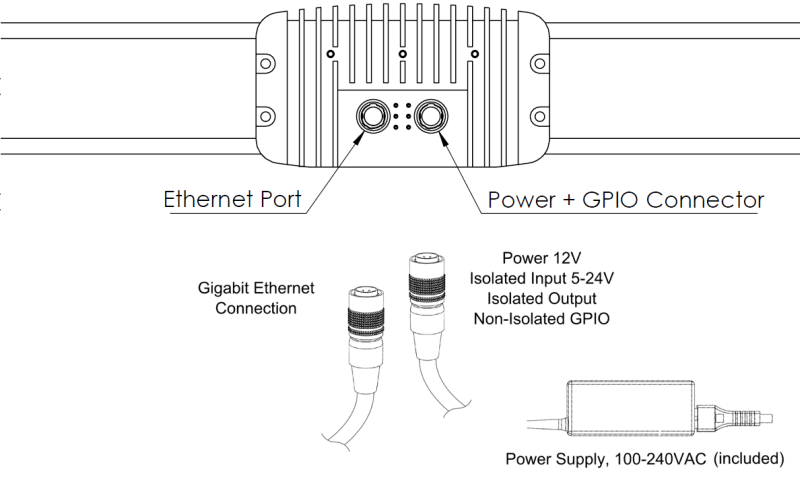
Connectivity
| Status LEDs meaning | |
|---|---|
| ⚫ Power status
Power cable connected |
⚫ Processing unit connected On => Suitable power connected |
| ⚫ Reserved
- |
⚫ Reserved
- |
| ⚫ Ethernet speed Off => Indicates 1 Gbps |
⚫ Ethernet activity Off => Link is down |
CAD data
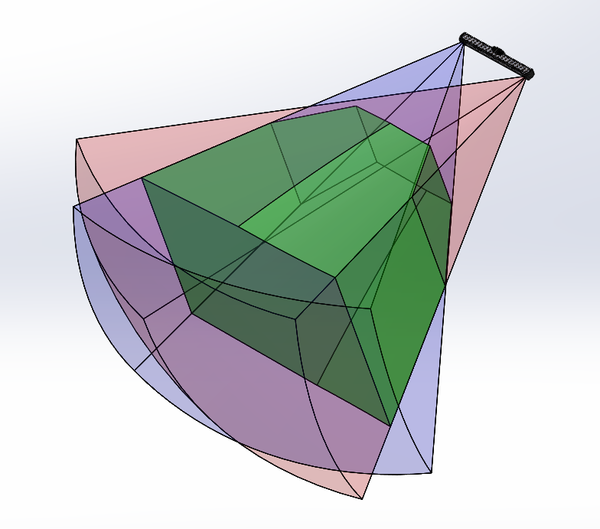
Contains 3D Scanner body and its scanning volume as a solid object.
Available CAD models for download:
| Device | Mounting space coordinate space | Camera coordinate space |
|---|---|---|
| PhoXi 3D Scanner XS | XS - mounting space | XS - camera space |
| PhoXi 3D Scanner S | S - mounting space | S - camera space |
| PhoXi 3D Scanner M | M - mounting space | M - camera space |
| PhoXi 3D Scanner L | L - mounting space | L - camera space |
| PhoXi 3D Scanner XL | XL - mounting space | XL - camera space |
| All in mounting space | All in camera space |
Note: Camera coordinate space is only approximate.
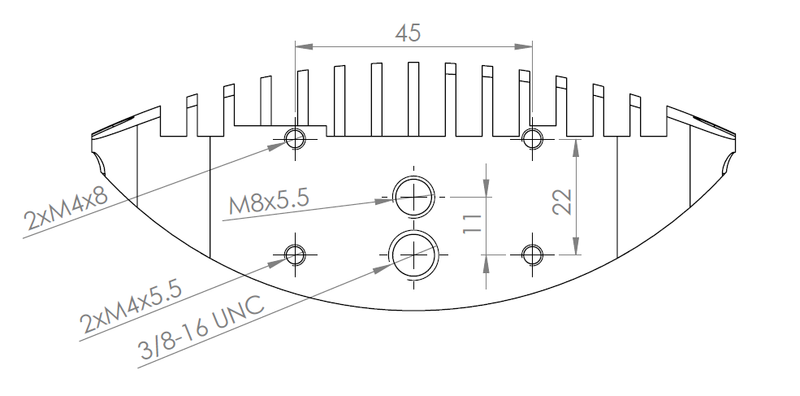
Mounting plate drawing
Connecting multiple scanners to one computer
- Using PhoXi Control
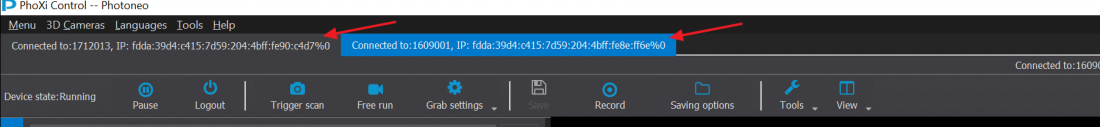
From version 1.2.X of PhoXi Control it is possible to connect to two scanners at the same time and trigger the scans one after another.
Connect to the first scanner, then click menu -> network discovery and then click the second scanner you want to connect to.
You will then have two tabs as you can see in the picture below and then you can change between the two tabs by clicking on them.
- Using the PhoXi API
Connecting mutliple scanners can also be done using the PhoXi API, you can download the example code for this here.
Important points to note are: 1)define SCANNER_HWID_1 and SCANNER_HWID_2 to the correct Hardware identification strings of your scanners
2)do not attempt to create 2 instances of pho::api::PhoXiFactory, instead create just 1 factory and call CreateAndConnect method twice to get 2 pointers to different scanners